The subject of nutrition is complex and varied. It encompasses everything from weight loss and gains to sports performance and supplements. Here we aim to give you a basic understanding of the requirements of a balanced diet and the importance of this in sport.
What does a balanced diet actually mean?
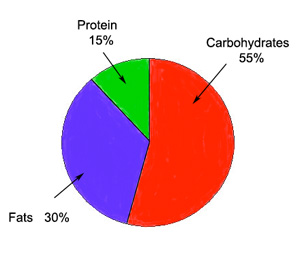
For most people a balanced diet should consist of: 60% Carbohydrates, 30% Fat, 10% Protein, Vitamins, minerals, and water, however, this does vary depending on the activity levels, type of exercise, and health status of the individual.
Carbohydrates
These are found in starchy and sugary foods. Complex carbohydrates are mainly starchy foods, including potatoes, rice, bread, and pasta, and have additional nutritional value as they contain many other vitamins, minerals, and fibre. Simple carbohydrates are the sugary ones, found in cakes, biscuits, and sweets which are sometimes termed empty calories, as they provide no other nutritional benefits.
Carbohydrates are our main source of energy, in fact, energy from the breakdown of carbs is the only type of energy the brain can use. Carbohydrates are broken down in the liver and muscles, by a process known as glycogenesis. It is then stored as glycogen until it is needed.
Sportspeople, especially those involved in endurance events often require higher than the normal 60% carbohydrate intake in order to maintain large stores of glycogen and resist fatigue.
Fats
Fats serve several important purposes. They provide energy and when stored, provide protection to our vital organs.
There are two types of fats, saturated and unsaturated. Saturated fats are ‘the bad fats’ which are normally solid at room temperatures, such as butter and meat fat. Unsaturated fat is more difficult to break down and so is mainly stored within the body. Unsaturated fats are generally better for us and are often liquid at room temperature, for example, olive oil and sunflower oil, although they can also be found in avocados and nuts.
A healthy diet should not contain more than 30% fat, and a maximum of 10% should be saturated fat. Fat provides a secondary source of energy and once the relatively small carbohydrate stores are exhausted, fat metabolism becomes the primary source of energy.
Proteins
Proteins are large compounds consisting of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids that the body requires. 12 of these can be synthesised within the body, and the other 8 (essential amino acids) must be consumed through our diets.
Proteins are found in abundance in meats, eggs, fish, dairy products, nuts, and seeds. Protein is essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of our body tissues, and for this reason, many athletes (mainly those requiring strength or size) will increase the amount of protein they consume, in order to help their muscles grow and develop strength.
Fibre
Fibre isn’t really a nutrient but you definitely need it in your diet to keep your digestive system healthy and working properly. It can be found in fruits and vegetables.
Fluids
Fluids are vital in any sport to help prevent dehydration. When we exercise our bodies sweat to help cool us down. This results in a loss of water which must be replaced so as to not inhibit performance. Electrolytes such as sodium are also lost in our sweat. For this reason, many sports drinks contain a mix of water and electrolytes. The presence of these electrolytes also helps the water to diffuse through the small intestine, back into the body.
Vitamin and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are vital in the diet for a wide range of functions but are only needed in tiny amounts. They are vital for chemical reactions and also to help our bones, skin, and teeth to grow
Fat-soluble vitamins such as Vitamin A and Vitamin D can be stored in the body. Vitamin A is found in vegetables, liver, and eggs, and Vitamin D is found in milk, fish, and eggs. Water-soluble vitamins cannot be stored in the body so we need to eat these in our diet, they include Vitamin C which is found in fruit and vegetables.
Minerals are also needed for healthy bones and teeth, as well as the growth of other tissues. They include things like Calcium which is found in dairy products and vegetables. Iron is found in liver, beans, and other green vegetables and is used for haemoglobin production in red blood cells.
Supplementation
There are so many types of supplements now widely available, but for most people, providing their diet is balanced and varied, supplementation is not necessary. Some athletes may want to supplement their diets to enhance their performance, especially when the difference between winner and runner-up can be a fraction of a second for a single millimeter. The most commonly taken supplements among athletes are protein and creatine.
Protein-based supplements are taken by those athletes wishing to increase their size and strength. Creatine is used by a wider band of athletes. It is promoted as a muscle performance enhancer as it is designed to allow repeated powerful muscle contractions. Creatine is naturally present within the body, it is used in the ATP-PC system of anaerobic energy production, where PC stands for Phospho-Creatine. Having excess stores of creatine enables this anaerobic energy system (and so a higher level of performance) to continue for longer.





